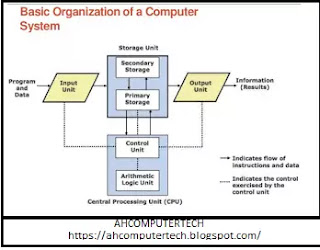
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION
Ø INPUT UNIT:
Data
and instructions must enter a computer system before the computer can perform
any computation on the supplied data. The input unit that links a computer with
its external environment performs this task. Data and instructions enter a
computer through an input unit in a form that depends upon the input device
used. For example, data can be entered using a keyboard in a manner similar to
typing and this differs from the way in which data is entered through a
scanner, another type of input device. However, a computer’s memory is designed
to accept input in binary code and hence, all input devices must transform
input signals to binary codes. Units called input interfaces accomplish this
transformation. Input interfaces match the unique physical or electrical
characteristics of input devices to the requirements of a computer system.
In
short, an input unit performs following functions:
(1.) It accepts (or reads) instructions and
data from outside world.
(2.) It converts these instructions and
data in computer acceptable form. Units called input interfaces accomplish this
task.
(3.) It supplies the converted instructions
and data to the storage unit for storage and further processing.
Ø OUTPUT UNIT:
An
output unit performs the revers operation of that of an input unit. It supplies
information obtained from data processing to outside world. Hence, it links a
computer with its external environment. As computers work with binary code, results
produced are also in binary form. Therefore, before supplying the results to outside
world, the system must convert them to human acceptable (readable) form. Units
called output interfaces accomplish this task. Output interfaces match the
unique physical or electrical characteristics of input devices (terminals,
printers etc.) to requirements of an external environment.
In
short, an output unit performs following functions.
(1.) It accepts the produced results, which
are in coded form. We cannot understand the coded results easily.
(2.) It converts these coded results to
human acceptable (readable) form. Units called output interfaces accomplish
this task.
(3.) It supplies the converted result to
outside world.
.
Ø
STORAGE UNIT:
Data
and instructions entered into a computer system through input units have to be
stored inside the computer before actual processing starts. Similarly, results
produced by a computer after processing have to be kept somewhere inside the
computer system before being passed on to an output unit. Moreover, a computer
must also preserve intermediate result for ongoing processing. Storage unit of
a computer system caters to all these needs. It provides space for storing data
and instructions, intermediate results, and results for output.
In
short a storage unit holds (stores):
(1.) The data and instructions required for
processing (received from input units).
(2.) Intermediate results of processing.
(3.) Final results of processing, before
the system releases them to an unit.
Storage unit
of all computers is comprised of following two types.
(1.) Primary Storage:
Primary
storage of a computer system, also known as main memory, stores pieces of
program instructions and data, intermediate results of processing, and recently
produced results of those job(s) on which the computer system is currently
working. The central processing unit can access these pieces information
directly at a very fast speed because they are represented electronically in
the main memory chip’s circuitry. However, primary storage is volatile, and it
loses the information in it as soon as the computer system switches off or
resets. Moreover, primary storage normally has limited storage capacity because
it is very expensive. Primary storage of modern computer systems is made up of
semiconductors devices.
(2.) Secondary Storage:
Secondary
storage of a computer system, also known as auxiliary storage, takes care of
the limitations of primary storage. It supplements the limited storage capacity
and volatile characteristics of primary storage. This is because secondary
storage is much cheaper than primary storage and it can retain information even
when the computer system switches off or resets. A computer system user
secondary storage to store program instructions, data, and information of those
jobs on which the computer system is currently not working but needs to hold
them for processing later. The most commonly used secondary storage medium is
magnetic disk.
Ø
ARITHMATIC AND LOGIC UNIT (ALU):
A computer performs all calculation
and comparison (decision-making) operations in the ALU. During processing of a
job, the computer transfers data and instructions stored in its primary storage
to ALU as and when needed. ALU does the processing and the computer temporarily
transfer intermediate results generated there back to primary storage until
needed later. Hence, data may move back and forth several times between primary
storage and ALU before processing of the job is over.
The engineering design of a computer’s
ALU determines the type and number of arithmetic and logic operations that a
computer can perform. However, almost all ALUs are designed to perform the four
basic arithmetic operations (add, subtract, multiply and divide) and logic
operations or comparisons such as, less than, equal to, and greaten than.
Ø CONTROL UNIT (CU):
How does an input device of a computer
system know that it is time for it to feed data to storage unit? How does its
ALU know what should be done with th data once it receives them. Moreover, how
it is that the computer sends only the results for output to an output device
and not the intermediate results? All this is possible due to the control unit
of the computer system.
A computer’s control
unit does not perform any actual processing of jobs, but acts as the central
nervous system for other components of the computer system. It manages and
coordinates the operations of all other components, It obtains instructions
from a program stored in main memory, interprets the instructions, and issues
signals causing other units of the system to execute them.
Ø CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT
(CPU):
Control Unit (CU) and arithmetic logic
unit (ALU) of a computer system are together known as the Central Processing
Unit (CPU). It is the brain of a computer system. Similarly, in a computer system
, the CPU performs all major calculations and comparisons, and also activates
and control the operations of other units of the computer.























No comments:
Post a Comment
Please do not enter any spam link in the comment box.